By Kim Smiley
A study recently published in the International Journal of Obesity found that infants given antibiotics before six months of age were 22 % more likely to be overweight between the ages of 10 months and 3 years. Researchers believe this may be because the natural balance of bacteria in their digestive tracts is altered by the antibiotics.
Obesity has long been assumed to be a matter of too much food into the body while too few calories are burned, but new studies. including the recent one finding a link between use of antibiotics early in life and body weight later in childhood, are suggesting that the issue may be more complicated than it appears on the surface.
 Scientists are still studying how bacteria in human digestive tracts affect how the body processes food, but many researchers believe that the balance of bacteria plays a role in how the body absorbs calories. The amount of calories that a body absorbs from the same amount of identical food may not be a constant. More studies are needed to understand the relationship between bacteria in the gut and body weight, but studies done so far are intriguing.
Scientists are still studying how bacteria in human digestive tracts affect how the body processes food, but many researchers believe that the balance of bacteria plays a role in how the body absorbs calories. The amount of calories that a body absorbs from the same amount of identical food may not be a constant. More studies are needed to understand the relationship between bacteria in the gut and body weight, but studies done so far are intriguing.
The link between antibiotics and higher body mass remained even when researchers controlled for factors such as what the baby ate, the weight of a baby’s parents, whether the mother smoked while pregnant, and the family’s socioeconomic status. Researchers did note that the study found an association and not a cause-effect link and that further studies are needed, but there seems to be a relationship between how antibiotics affect the body and body mass.
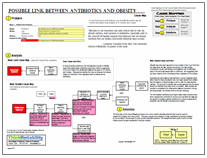
More research is needed to fully understand this issue, but this study is an interesting step to better understanding the causes of childhood obesity. On the downloadable PDF, we have created a Cause Map, or visual root cause analysis, to show the possible cause-and-effect relationships between use of antibotics in early enfancy and childhood obesity.
In this specific study used to build this example, the researchers were quick to point out that infants should be given antibiotics if they are needed, but it’s important to understand how the medication may be affecting bodies, especially very young bodies.
To view a Cause Map of this issue, click on “Download PDF”.

