![]() Outrage over rampant increases in drug prices is nothing new. But it seems to have reached a new high with the rising cost of the EpiPen, an auto-injection device that delivers epinephrine to severe allergy sufferers who are at risk of their throat closing shut due to anaphylaxis. Disgust with the increase is at such levels that Martin Shkreli, the CEO of Turing, who, in 2015, raised the price of Daraprim, a malaria-HIV drug 5,000% (from $13.50 to $750 a tablet) has asked “What drives this company’s moral compass?” and referred to Mylan (the manufacturer of the EpiPen®) as “vultures”. (See our previous blog on the price increase of Daraprim.)
Outrage over rampant increases in drug prices is nothing new. But it seems to have reached a new high with the rising cost of the EpiPen, an auto-injection device that delivers epinephrine to severe allergy sufferers who are at risk of their throat closing shut due to anaphylaxis. Disgust with the increase is at such levels that Martin Shkreli, the CEO of Turing, who, in 2015, raised the price of Daraprim, a malaria-HIV drug 5,000% (from $13.50 to $750 a tablet) has asked “What drives this company’s moral compass?” and referred to Mylan (the manufacturer of the EpiPen®) as “vultures”. (See our previous blog on the price increase of Daraprim.)

The US Senate has demanded information related to the cost increase. It’s not based on the cost of raw materials (the amount of epinephrine in an EpiPen costs less than a dollar). Mylan claims that it’s due to an improved product, but provides no specifics, and there doesn’t appear to be anything noticeably different to users. Many claim that the price increase is simply because Mylan can. Senator Amy Klobuchar, the ranking member of the Senate Judiciary Committee, says “This outrageous increase in the price of EpiPens is occurring at the same time that Mylan Pharmaceutical is exploiting a monopoly market advantage that has fallen into its lap.”
Mylan currently has an effective monopoly on the EpiPen. There is no generic alternative. EpiPen has a monopoly in the US via patent until 2025. Another manufacturer’s application to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) was rejected for “major deficiencies”. It does not expect its product to be brought to market until 2017 at the earliest. Three alternatives to the EpiPen have been removed from the market since 2012 although one, Adrenaclick, is back on the market. However, Adrenaclick is not considered pharmaceutically equivalent, so it has to be prescribed by a doctor, which is unlikely due to the name recognition of EpiPen (thanks to its massive marketing campaign and free giveaways). It’s also considered more difficult to use, somewhat expensive on its own, and not covered by many insurance plans.
Mylan says that “In 2015, nearly 80% of commercially insured patients using the My EpiPen Savings Card received EpiPen Auto-Injector for $0.” That leaves nearly 20% of insured patients (and nearly all uninsured patients) paying out-of-pocket costs that have been reported at more than $1,000 for a two-pack (the only way EpiPens are currently sold – many times two doses are needed). To add insult to injury, an EpiPen is usually good for a year or less because epinephrine is extremely unstable and a full dose is needed in the case of a reaction.
Unfortunately, there aren’t many good alternatives to paying for the EpiPen. Going without, or using an expired EpiPen, could be extremely dangerous. While epinephrine can be injected via a normal syringe without the EpiPen functionality, that in itself carries risk and should only be performed by a trained professional. (Many governments are providing epinephrine, syringes and training to emergency medical responders to avoid the cost of multiple EpiPens.)
Most of the general public will just have to wait: for a generic to be introduced, for Adrenaclick to be covered by insurance, or for the Senate to quash the price gouging.
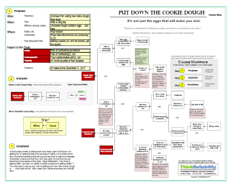
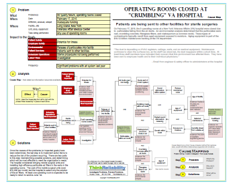
To view a one-page PDF showing the cause-and-effect relationships associated with the EpiPen price increases, click “Download PDF” above. Or, click here to read more.